How to setup AWS RDS database with Flask-SQLAlchemy
Introduction
Flask-SQLAlchemy is an extension for Flask that adds support for SQLAlchemy to your application. SQLAlchemy is a Python library designed to simplify data access and manipulation. In other words, it helps programmers build applications that interact with databases.
SQLAlchemy is a powerful tool for building object oriented applications. It provides a clean interface for defining database schemas and mapping between those schemas and Python classes.
In this tutorial, we will look at how you can use Flask-SQLAlchemy with your AWS RDS database.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- SQLAlchemy Architecture
- Flask-SQLAlchemy
- Flask-SQLAlchemy with AWS RDS
- Database Connectivity
SQLAlchemy Architecture
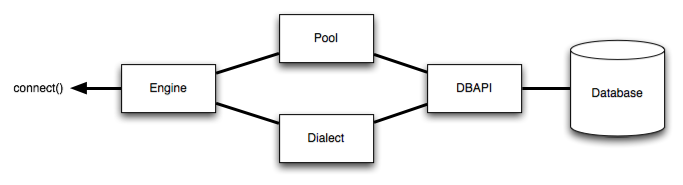
The Engine is at the heart of the SQLAlchemy library. At a high level, the engine takes input from our Python application and processes the information and converts it into output understood by our SQL database.
The engine internally references a Dialect object that handles communication and a Pool object that handles connections. These in turn work with DBAPI behind the scenes to translate data to and from our app/database. The following architecture diagram illustrates the structure ([source][https://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/14/core/engines.html]).
Database URL
The Engine expects a Database URL as input during instantiation. The format of the URL is as follows:
dialect+driver://username:password@host:port/database
Key elements of the URL are:
- dialect: Type of database like sqlite, mysql or postgresql
- driver: Name of the DBAPI to be used to connect to the database. It is an optional field and if not specified, a default DBAPI will be imported if available. For e.g.,
psycopg2is the default DBAPI forpostgresql. - username & password: Credentials for your database
- host & port: Where your database is running
- database: The database that you want to connect to
Flask-SQLAlchemy
Flask-SQLAlchemy is a Flask specific extension that makes it simpler to use and interact with SQLAlchemy.
You can start using SQLAlchemy by adding the following code:
from flask import Flask
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:////tmp/test.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
Things to note:
- SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI: This refers to the Database URL that is provided as input to the SQLAlchemy engine.
- db: This db object can be run any database operations like creating and updating tables.
Flask-SQLAlchemy with AWS RDS
Now that we have a good understanding of how to setup Flask-SQLAlchemy, let’s look at how we can setup our application to interact with AWS RDS.
- dialect: Whether you are using a MySQL or Postgres Database.
- username & password: Credentials that you setup during the creation of the database
- host & port: Can be found out via the AWS RDS console under the connectivity tab.
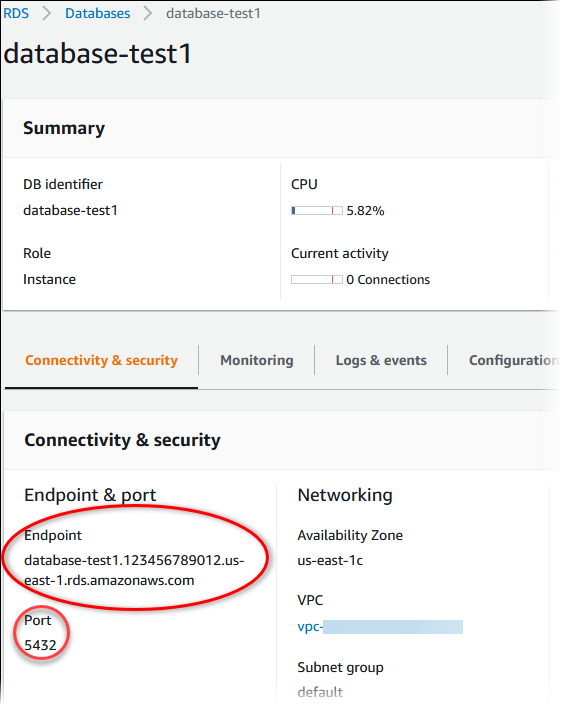
Let’s look at a few examples of what SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI would look like for your AWS RDS Database:
Postgres
postgresql://user:[email protected]:5432/mydatabase
MySQL
mysql://user:[email protected]:3306/mydatabase
Database Connectivity
Once your RDS database is up and running, we need to ensure connectivty is set up correctly so that your application can access the database.
If your DB instance is publicly accessible, make sure its associated security group has inbound rules for the IP addresses that you want to access it.
If your DB instance is private, make sure its associated security group has inbound rules for the security group of each resource that you want to access it, such as the security group of an Amazon EC2 instance.
Due to security reasons, try to only allow trusted IPs and / or security groups access to your database.